A service is identified by combining three aspects:
-
The element (part) of testing
-
The activity that is executed
-
The responsibility of the organisation.
The test process consists of many process elements, which each in turn consist of elements (sub-process elements). These
elements can be identified in different ways. For instance by looking at the phases and sub-activities within TMap. Another
option is to look at the products that are delivered. There is no set list of elements. Examples are:
-
Master test plan
-
Test scripts
-
Tests
-
Defect management tool
-
The test execution phase
-
Test script automation
-
Defect management
-
Setting up test environment.
5 activities can be executed for each element, i.e.
-
Support (presentation, training, coaching, advice)
-
Checking (quality checking, executing audit, reviewing)
-
Preservation (administration, maintenance)
-
Execution (execution, coordination)
-
Research & development (development, implementation).
The organisation may bear responsibility for each combination of sub-element and activity. Three types of
responsibility can be distinguished. In ascending order, these are: None, Obligation of effort, Obligation to deliver
results.
-
No obligation - The permanent test organisation delivers the required expertise on the basis of the request (if
present and available). There is no obligation or responsibility as to how the request is to be answered.
-
Obligation of effort - The permanent test organisation must deliver the required effort on the basis of the
request. The delivery must occur within a pre-defined timeframe. The permanent test organisation is responsible for
guaranteeing continuity in delivering the effort.
-
Obligation to deliver results - The permanent test organisation must deliver a result on the basis of the request.
The delivery must occur within the pre-defined timeframe, at pre-defined costs, and at a pre-defined quality level.
The permanent test organisation is responsible for guaranteeing continuity in delivering the result.
These three aspects of element, activity and responsibility identify a service. The service matrix is created by
entering them in a table. The matrix describes the various testing elements in the left-hand column. The topmost row
shows the activities. The junctions contain the responsibility of the test organisation.
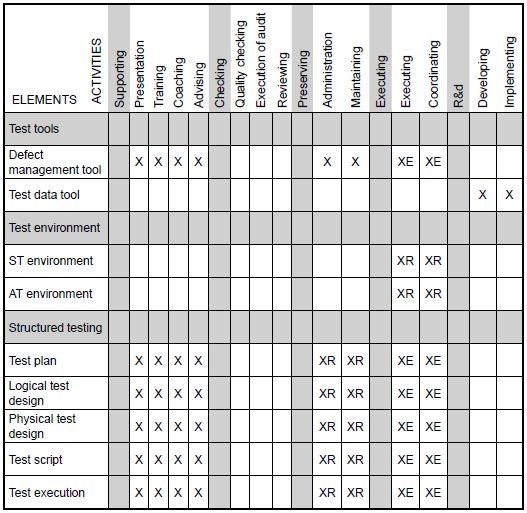
Table 1: an example of the service matrix.
X = Service without obligation
XE = Service with obligation of effort
XR = Service with obligation to deliver results
|